
Hochbaum DS, Landy D (1997) Scheduling semiconductor burn-in operations to minimize total flowtime. Haupt R (1999) A survey of priority rule-based scheduling. Int J Prod Res 20:27–45ĭabbas R, Fowler JW (2003) A new scheduling approach using combined dispatching criteria in wafer fabs. In: Advance semiconductor manufacturing conference IEEE/SEMI, pp 148–154īlackstone JH, Phillips DT, Hogg GL (1982) A state-of-the-art survey of dispatching rules for manufacturing job shop operations. Comput Oper Res 31:397–414īixby R, Burda R, Miller D (2006) Short-interval detailed production scheduling in 300 mm semiconductor manufacturing using mixed integer and constraint programming. Math Comput Model 33:363–383īilge Ü, Kırac F, Kurtulan M, Pekgün P (2004) A Tabu search algorithm for parallel machine total tardiness problem. Comput Oper Res 26:127–141īank J, Werner F (2001) Heuristic algorithms for unrelated parallel-machine scheduling with a common due date, release dates, and linear earliness and tardiness penalties. Prod Plan Control 9:690–699īalakrishnan N, Kanet JJ, Sridharan SV (1999) Early/Tardy scheduling with sequence dependent setups on uniform parallel machines.

In: Advance semiconductor manufacturing conference IEEE/SEMI, pp 188–193Īrzi Y, Raviv D (1998) Dispatching in a workstation belonging to a re-entrant production line under sequence-dependent set-up times. In particular, our method usually gives solutions very close to the exact optimum for smaller scheduling problems, and calculates good solutions for scheduling up to 200 jobs on 40 machines within 10 min.Īltendorfer K, Kabelka B, Stöher W (2007) A new dispatching rule for optimizing machine utilization at a semiconductor test field. Our computational experiments indicate that EDDLC and our proposed reoptimization techniques are very efficient and effective. In order to handle real-world large-scale scheduling problems, we propose an efficient dispatching rule that assigns a job of the earliest due date to a machine with least recipe changeover (EDDLC) and try to re-optimize the solution by local search heuristics which involves interchange, translocation and transposition between assigned jobs. We then propose a technique to estimate the upper bound for the number of jobs processed by a machine, and use it to effectively reduce the size of the MIP formulation. Although our polynomial-sized MIP formulation can correctly model this scheduling problem, it is so difficult that even a feasible solution can not be calculated efficiently for small-scale problems.
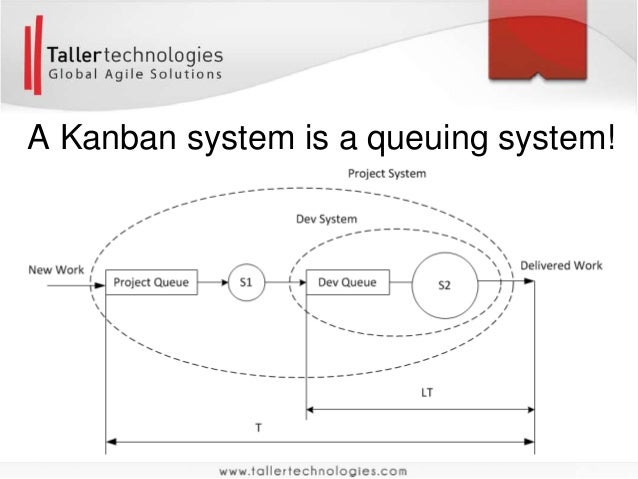
We propose a mixed integer programming (MIP) formulation which treats tardy jobs as soft constraints so that our objective seeks the minimum weighted sum of makespan and heavily penalized tardy jobs. We investigate a difficult scheduling problem in a semiconductor manufacturing process that seeks to minimize the number of tardy jobs and makespan with sequence-dependent setup time, release time, due dates and tool constraints.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
